Physics prefixes explained in detail
Physics prefixes explained in detail
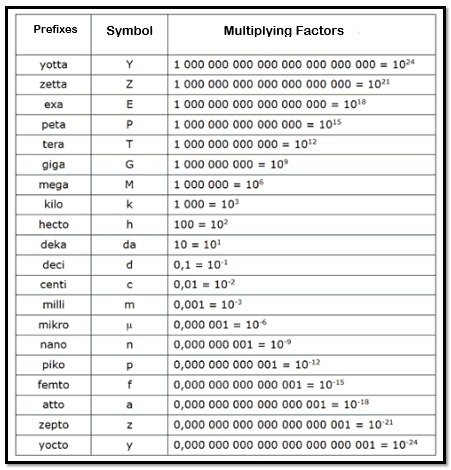
Physics prefixes explained in detail
Define prefixes?
A prefix is a collection of symbols or letters that are added to the start of a word to change its meaning. Prefixes are used to express very big or very small values in the context of engineering and science, which makes it simpler to work with various orders of magnitude.
Prefixes that are frequently employed in the fields of science and engineering are as follows:
1. deca(da):
The prefix "deca-" is a metric system prefix that denotes a factor of 10.
It comes from the Greek word "deka," which means "ten." When added as a prefix to a base unit, "deca-" indicates that the quantity is multiplied by 10. For example:
Decameter (dam): 1 decameter is equal to 10 meters.
Decagram (dag): 1 decagram is equal to 10 grams.
Decaliter (dal): 1 decaliter is equal to 10 liters.
It's worth noting that the use of the "deca-" prefix is not as common as some other metric prefixes like kilo-, centi-, or milli.
2. hecto- (h):
The prefix "hecto-" is a unit prefix in the metric system denoting a factor of 100.
It comes from the Greek word "hectos," meaning "hundred." When used with a base unit, such as meters or grams, "hecto-" indicates that the measurement is multiplied by 100.
For example, one hectometer (hm) is equal to 100 meters, one hectogram (hg) is equal to 100 grams.
and one hectoliter (hl) is equal to 100 liters. The symbol for "hecto-" is "h."
3. Kilo (k):
This prefix stands for a 1,000-fold multiplier. For instance, 1,000 grammes make up one kilogramme (kg).
The prefix "kilo-" is derived from the Greek word "khilioi," which means "thousand."
The kilo-prefix in the International Standard of Units (SI) denotes a 1,000-fold multiplication. It is indicated by the letter "k."
The following are some instances of quantities with the prefix kilo:
The kilogramme (kg) In the SI system as well, the kilogramme serves as the basic unit of mass. There are 1,000 grammes in a kilogramme.
A kilometre is a unit of measurement for both length and distance. There are 1,000 metres in a kilometre.
Power is measured in kW, or kilowatts. There are 1,000 watts in a kilowatt.
Digital information is measured in kilobits (kb), or kilobytes. There are 1,000 bits in a kilobit.
The kilohertz (kHz) is a measurement of frequency. There are 1,000 hertz in a kilohertz.
The kilo-prefix is frequently employed to represent amounts that exceed the base unit but are still practicably achievable. It offers a handy way to talk about amounts that are roughly 1,000 times higher than the basic unit.
4. Mega- (M):
This prefix stands for a millionfold factor. One megawatt (MW), for instance, is equal to one million watts.
In the International System of Units (SI), the prefix mega- is frequently used to indicate a factor of one million, or 10^6.
It comes from the Greek adjective "megas," which means "great" or "large." When describing quantities or measurements that are considerably bigger than the base unit, the mega-prefix is used.
A megabyte (MB), in the context of digital storage, is a measure of data size equivalent to roughly one million bytes.
The terabyte (TB) is equal to one trillion bytes, just as the gigabyte (GB) is equal to one billion bytes.
In the field of telecommunications, the prefix mega- is used to express data transfer rates.
For example, a megabit per second (Mbps) represents one million bits transmitted in one second.
Higher prefixes like gigabit per second (Gbps) and terabit per second (Tbps) are also used to indicate even faster data transfer rates.
Additionally, mega- can be applied to other measurements, such as megahertz (MHz) in electronics, which signifies one million cycles per second in a wave or oscillation. It is also used in megaohms (MΩ) to denote resistance in electrical circuits.
Overall, the mega- prefix is widely used across various fields to represent values that are significantly larger than the base unit, typically on the scale of millions or billions.
5. Giga (G) :
A factor of a billion is identified by the term giga (G). One gigahertz (GHz), for instance, is equivalent to one billion hertz.
The term "giga" is a prefix in the International System of Units (SI) denoting a factor of 10^9, or one billion. It is derived from the Greek word "gigas," meaning giant. The symbol for giga is "G."
"Giga" is commonly used in the fields of computer science, telecommunications, and data storage to represent large quantities or capacities.
For example, a gigabyte (GB) is approximately one billion bytes, and a gigahertz (GHz) represents one billion cycles per second in the context of computer processor speed.
In telecommunications, "gigabit" (Gb) refers to a data transfer rate of one billion bits per second.
while "gigabit per second" (Gbps) represents a transfer speed of one billion bits per second.
Overall, the prefix "giga" indicates a significant scale or magnitude, typically referring to a billion or a large quantity or capacity in various scientific and technological contexts.
6. Tera (T):
This prefix stands for a trillion-fold multiplier. One terabyte (TB), for instance, is equal to one trillion bytes.
"Tera" is a prefix used in the International System of Units (SI) to denote a factor of 10^12, which is equal to one trillion.
The term "tera" originates from the Greek word "teras," meaning "monster" or "gigantic." It is commonly used in various fields of science and technology to express large quantities or magnitudes.
For example, a terabyte (TB) represents approximately one trillion bytes of data, and a terawatt (TW) is equivalent to one trillion watts of power.
The "peta-" and "exa-" prefixes are used in the International System of Units (SI) to denote very large quantities of measurement. Here's how they are defined:
7. Peta- ( P):
This prefix represents a factor of 10^15, which means one quadrillion or one million billion.
The term "peta" is derived from the Greek word "penta," which means five. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000 or 1 x 10^15.
Examples of the use of the "peta-" prefix:
A petabyte (PB) is approximately one quadrillion bytes.
A petahertz (PHz) represents one quadrillion hertz.
8. Exa- ( E):
This prefix represents a factor of 10^18, which means one quintillion or one billion billion.
The term "exa" is derived from the Greek word "hexa," which means six. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 or 1 x 10^18.
Examples of the use of the "exa-" prefix:
Exabytes (EB) are roughly one quintillion bytes.
An exahertz (EHz) represents one quintillion hertz.
These prefixes are commonly used in scientific, technological, and computing contexts to express large quantities of data storage, data transfer rates, frequencies, and other measurements on a massive scale.
9. Zetta- (Z):
Zetta represents a factor of 10^21, which is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000. It is often used in contexts such as data storage capacity or energy consumption on a global scale.
10. Yotta- (Y):
Yotta is the largest decimal prefix in the International System of Units (SI). It denotes a factor of 10^24, which is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000. This prefix is typically used when dealing with astronomical distances or large-scale measurements in cosmology.
11. deci(d):
The prefix "deci-" in the metric system represents a factor of 0.1 or one-tenth.
The Latin term "decimus," which means ninth, is where it got its name.
When added as a prefix to a base unit, it creates a new unit that is one-tenth the size of the base unit.
For example:
1 decimeter (dm) = 0.1 meter (m) 1 deciliter (dL) = 0.1 liter (L) 1 decigram (dg) = 0.1 gram (g)
So, the prefix "deci-" is used to denote a unit that is one-tenth of the base unit.
12. centi(c):
The prefix "centi-" is derived from the Latin word "centum," meaning "one hundred." In the International System of Units (SI), the centi- prefix represents a factor of one-hundredth, or 1/100. It is symbolized by the lowercase letter "c."
For example, if we take the base unit of length, the meter, a centimeter (cm) is equal to one-hundredth of a meter. Similarly, a centiliter (cl) is one-hundredth of a liter, and a centigram (cg) is one-hundredth of a gram.
Here are a few more common examples of units using the centi- prefix:
Centimeter (cm): 1 cm = 0.01 meter
Centigram (cg): 1 cg = 0.01 gram
Centisecond (cs): 1 cs = 0.01 second
Centiliter (cl): 1 cl = 0.01 liter
Centigray (cGy): 1 cGy = 0.01 gray (a unit of radiation absorbed dose)
The centi- prefix is commonly used in measurements where a smaller unit is needed, but still larger than a milli- (one-thousandth) or micro- (one-millionth).
13. mili( m):
The prefix "mili-" is derived from the Latin word "millesimus," meaning "thousandth." It is used in the metric system to denote a factor of one thousandth (1/1000) or 0.001.
For example:
the millimeter (mm) is one-thousandth of a meter (1/1000 m), and the milligram (mg) is one-thousandth of a gram (1/1000 g).
Similarly, the milliliter (mL) is one-thousandth of a liter (1/1000 L).
The symbol for the prefix "mili-" is "m" (lowercase) and is always written in front of the base unit symbol. It indicates that the value is divided by 1000 to convert it to the base unit.
14. Micro- (µ):
This prefix denotes a factor of 1/1,000,000 or 10^-6. For example, 1 microsecond (µs) is equal to 1 millionth of a second.
The prefix "micro-" means small or tiny. It is derived from the Greek word "mikros," which means small or little.
In the metric system, "micro-" represents one millionth (1/1,000,000) of a unit.
For example, a microgram is one millionth of a gram, and a micrometer is one millionth of a meter. The use of the prefix "micro-" is common in various fields, including science, technology, and medicine, to indicate something that is on a very small scale.
15. Nano- (n):
This prefix denotes a factor of 1/1,000,000,000 or 10^-9. For instance, 1 nanometer (nm) is equal to 1 billionth of a meter.
The prefix "nano-" is derived from the Greek word "nanos," meaning "dwarf" or "very small." In the International System of Units (SI), the prefix "nano-" represents a factor of 10^-9 or one billionth (1/1,000,000,000). It is commonly used in the fields of science and technology to denote extremely small measurements or quantities.
For example, a nanometer (nm) is equal to one billionth of a meter, and a nanosecond (ns) is one billionth of a second. The prefix "nano-" is also used in terms like nanotechnology, nanoscience, and nanomaterials, which refer to the study and manipulation of matter at the nanoscale.
16. Pico- (p):
This prefix denotes a factor of 1/1,000,000,000,000 or 10^-12. For example, 1 picosecond (ps) is equal to 1 trillionth of a second.
The prefix "pico-" is a metric prefix in the International System of Units (SI) denoting one trillionth (1/1,000,000,000,000) or 10^-12. The letter "p" is used to denote it.
Here are a few examples of its usage:
A picosecond (ps) is a unit of time equal to one trillionth of a second.
A picogram (pg) is a unit of mass equal to one trillionth of a gram.
. A picometer (pm), or trillionth of a metre, is a unit of length.
17. Femto- (f):
This prefix denotes a factor of 1/1,000,000,000,000,000 or 10^-15. For instance, 1 femtosecond (fs) is equal to 1 quadrillionth of a second.
The prefix "femto-" is a metric prefix in the International System of Units (SI) denoting a factor of 10^-15.
From the Danish term "femten," which means fifteen, comes this word. In scientific and engineering notation, the symbol for the femto- prefix is "f."
Here are some common units and measurements that use the femto- prefix:
Femtosecond (fs): One femtosecond is equal to one quadrillionth (or one millionth of a billionth) of a second. It is commonly used in ultrafast laser spectroscopy and studies of chemical reactions on extremely short timescales.
Femtometer (fm): One femtometer is equal to one quadrillionth (or one millionth of a billionth) of a meter. It is often used in nuclear physics to measure the size of atomic nuclei.
Femtocoulomb (fC): One femtocoulomb is equal to one quadrillionth (or one millionth of a billionth) of a coulomb. The coulomb is the unit of electric charge, and the femtocoulomb is used to describe extremely small charges, such as those found in electronic circuits or subatomic particles.
Femtojoule (fJ): One femtojoule is equal to one quadrillionth (or one millionth of a billionth) of a joule. The joule is the unit of energy, and the femtojoule is used to describe very small amounts of energy, such as in nanoscale electronic devices or energy transfer processes at the molecular level.
These are just a few examples of how the femto- prefix is used. It is important to note that the SI system provides a standardized way to express measurements, making it easier to communicate and compare quantities across different scientific and engineering fields.
18. atto(a):
The prefix "atto-" is a metric prefix in the International System of Units (SI) denoting a factor of 10^-18.
It comes from the Danish term "atto," which means 18 in English. The symbol for the atto- prefix is "a."
Here are some examples of its usage:
An attosecond (as) is equal to one billionth of a billionth of a second (10^-18 seconds). It is used to measure extremely short time intervals, particularly in the field of ultrafast optics and atomic physics.
Attometer (am) represents a length unit equal to one billionth of a billionth of a meter (10^-18 meters). It is used to describe atomic and subatomic scales.
The attowatt (aW) is a unit of power equal to one billionth of a billionth of a watt (10^-18 watts). It is commonly used in discussions involving very small amounts of power, such as in nanotechnology or quantum computing.
The atto- prefix is one of the smallest SI prefixes, indicating extremely small quantities or measurements.
19. zepto(z):
The term "zepto" is a prefix used in the International System of Units (SI) to denote a factor of 10^-21. It is derived from the Greek word "zepto," which means "seven." The symbol for zepto is "z." Here are some commonly used units that incorporate the zepto prefix:
Zeptosecond (zs): One zeptosecond is equal to one trillionth of one billionth of a second (10^-21 seconds). It is used in the field of ultrafast science to measure extremely short time intervals.
Zeptometer (zm): One zeptometer is equal to one trillionth of one billionth of a meter (10^-21 meters). It is used to describe extremely small distances at the atomic and subatomic scale.
20. yocto(y):
The yocto- prefix is a decimal unit prefix in the International System of Units (SI), denoting a factor of 10^(-24). It is the smallest SI prefix and is rarely used in everyday contexts due to its extremely small value.
The prefix "yocto-" is derived from the Greek word "okto," meaning eight, and signifies a factor of 10^(-24), which is equivalent to dividing by 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000.
The yocto- prefix is typically used in scientific and technological fields to describe quantities that are extremely small.
For example, it may be used to denote the size of subatomic particles or the energy levels of photons.
What's Your Reaction?





















