Distance and displacement
Distance and displacement
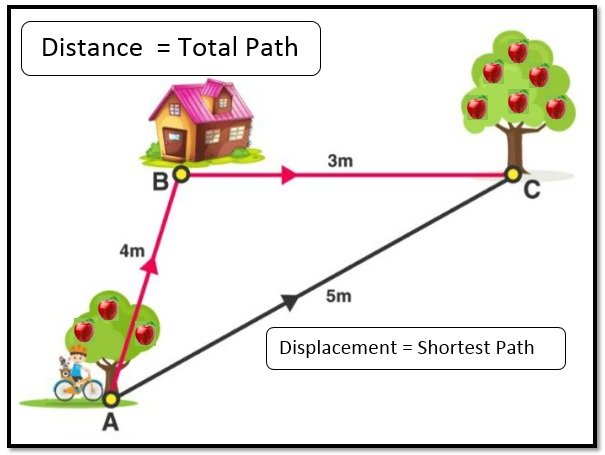
Distance and displacement
These are two quantities that look the same but are completely different with different meanings and definitions. One is a measure of "how much ground an object has traveled during its movement", while other is a measure of "how far an object is".
In this article let us understand the difference among them.
Distance
It is a numerical value that quantifies the path between two points or objects in space. In everyday usage, it usually refers to the physical length between two points.
For example, when we say the distance between two cities is 100 kilometers, we mean the length of the road or direct route connecting them.
Example:
Suppose you are planning a trip from city A to city B. The two cities are 500 km apart. In this case, distance is the length of road you have to travel to get to your destination.
During your journey you will drive for several hours, passing cities, landscapes and various points of interest. You will come across highways, small roads and maybe even some detours. Whichever route you choose, the gap between city A and city B remains the same at 500 kilometers. This is a measure of the distance of two locations and does not change depending on the route you take.
Which quantity it is ?
Unit:
Distance is a fundamental concept in math, physics and other scientific disciplines. It can be measured in different units such as meters, kilometers, miles or any other suitable unit of length.
Calculation:
It can be calculated using different methods, depending on the context and geometry of the space involved. It provides a quantitative measure of the spatial relationships among objects or locations and is critical to understanding spatial dimensions, motion, and relationships between objects in different areas of study.
Formula:
d= d1+d2
Displacement
It is the It represents the change in an object's position from its starting point to its ending point. It is a measure of the distance and direction in a straight line between the start and end position of an object.
Formula:
It is symbolized as Δx and is calculated by subtracting the start position (x₁) from the end position (x₂) of the object:
Δх = x₂ - x₁
Here
x₂= final point
x₁= initial point
The resulting value can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on the direction and amount of movement. A positive value means that the object has moved in a positive direction along the selected coordinate system, while a negative value means that the object has moved in the opposite (negative) direction. A zero result means that the position has not changed; the object remains in the same place.
Imagine you are on the starting line of a track. Run 100 yards east, turn around and run back 50 yards west. In this scenario, the shift is a sharp change in your location from your starting point to your ending point, regardless of which path you take.
Example:
To calculate the displacement, we need to consider both the distance traveled and the direction. In this case, you ran 100 yards east and then 50 yards west. Since east and west are opposite directions, we subtract the distance traveled from one point to other.
Δх = Distance East - West
= 100 meters - 50 meters
= 50 meters to the east
Therefore, the answer in this example is 50 meters east. It represents a straight line between the start and end point, taking into account the direction of travel.
Which quantity it is?
It is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude (distance) and direction. It is often used in physics to describe the change in an object's position from one point to another.
| Parameters | Distance | Displacement |
| Defination | Full path or complete path covered by the object. | The shortest distance between an object's ultimate position and its starting point during motion. |
| Type of quantity |
This is a scalar value. It depends upon magnitude only. |
This is a vector quantity. It depends both on magnitude and direction. |
| Increase/decrease | It does not decrease with time. | With time, it can increase or decrease. |
| Greater/lesser | It is never less than the displacement offset value. | It is either less than or equal to the distance. |
| Symbol | d is symbol for distance. | Δх |
| Information received | It provides detailed information on the path that the object took. | It does not provide comprehensive information regarding the object's travel. |
What's Your Reaction?





















