Physics Circular Motion

Definition:
It is defined as the movement of an item while rotating in a circle. They can take many different forms, including rotation, rectilinear, oscillation, uniform, and periodic.
List of Variables:
1)Angular Displacement:
The angle the object travels from its initial location to its ultimate position in a predetermined amount of time is referred to as angular displacement.
Pictured is the Angle of departure, which indicates AOB.
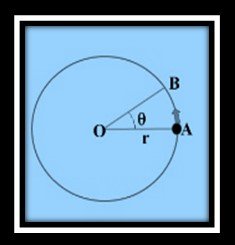
Radian (rad) is its unit.
2)Angular Velocity:
It is represented by the symbol "ω" and determined by the angular velocity (angular displacement).
ω=angular displacement/time
ω=dθ/dt
Radian per second (Rad/sec) is the unit used.
It is the rate at which angular velocity varies with respect to "t".
α = d ω/ d t.
Rad/ sec2 is its measure.
Period:
The total amount of time it takes a wave to undergo each oscillation is referred to as the time period. An occurrence is referred to as periodic if it occurs frequently. The period is the amount of "t" it takes for a periodic event to repeat itself.
ω=θ/t
θ=2π and T=t
ω=2π/T
T=2π/ω
Frequency
Frequency is the overall measure of how many wave cycles there are in a second. "f" is a symbol for frequency. the SI unit if the frequency is in hertz or per second. The sound frequency of a human, for instance, is 20 hertz if they create 20 sound waves in a second.
f=1/T
Types:
It can be divided into two main types: uniform and non-uniform.
a)Uniform Circular Motion:
When an object travels in a round direction at a fixed speed, it exhibits uniform circular motion. In this type, an object travels equal distances in equal time intervals. The magnitude of the object's velocity remains constant, but its direction is constantly changing, always perpendicular. Towards the circle's center, a centripetal force is needed to keep this going. Examples include a satellite orbiting a planet or a car moving at a constant speed on a circular orbit.
Non-uniform Circular Motion:
It occurs when an object moves in a circular path but at a variable speed. In this type, an object travels unequal distances in equal time intervals. The amount and direction of the object's velocity are constantly changing. The acceleration is directed toward the center and is responsible for the change in the object's velocity. Examples include a car traveling at different speeds on a winding road or a roller coaster traveling on a track with loops and turns.
Daily Life Examples:
There are several examples from everyday life. Here are some of them:
Tires: When the car is moving, the tires rotate around as the car moves forward. The movement of the wheels allows the car to roll and move smoothly on the road.
Washing machine: The drum of the washing machine rotates during the wash and spin cycles. This helps to effectively shake and clean your clothes.
Stirring a cup of coffee: When you stir a cup of coffee with a spoon, the spoon moves. The circular motions help blend the coffee and ensure that the sugar and cream are evenly distributed throughout the liquid.
Roller coasters: Roller coasters often have loops or corkscrew elements. As the roller coaster moves around the track, it goes through loops or hoops, providing an exciting experience for riders.
Pendulum Clock: The swinging motion of the pendulum in the clock. The pendulum swings back and forth in an arc, creating a smooth, rhythmic motion that regulates the movement of the clock's movements.
Ferris Wheel: The driver has a comprehensive view of the surrounding area as the passenger cabins move in a circular motion as the wheel spins.
The movement of a satellite around the planet is shown in a fixed orbit, which is usually circular. Thus, the movement of satellites in orbit is another example of everyday life.
Stone tied to a rope: When a force is applied to a wire attached to a stone at one end, by twisting it in the air, the stone rises in height and describes a path. This clearly demonstrates the existence of circular motion. There is a special kind of force acting on the stone, known as a centripetal force, that keeps the stone circulating.
Mix dough: To stir cake batter or tea, the stirring spoon tends to follow a round path equidistant from the center. Therefore, the movement of the spoon is a circular motion. A number of mechanical mixing or whipping devices have also been invented. The blades of such agitators tend to circulate in a similar fashion but at a higher speed for better performance.
The movement of electrons around the nucleus: The electrons of an element revolve around the nucleus in their orbits. An orbit is the trajectory of an electron around the nucleus. The core serves as the center here and the orbit has a circular character. Therefore, the movement of electrons is a circulatory movement.
Rotation of the lasso: The human lasso trick is a classic example of a circulation move. To perform a lasso trick, a person tends to make circular movements with the hand. This completely tightens the string and creates a significant pull in it. The continuous movement of the arm in a circle helps keep the rope moving and prevents it from falling to the floor.
What's Your Reaction?





















