Terminal Velocity
Terminal velocity, discovered by Galileo, is the maximum speed an object can descend through a liquid, determined by mass, gravity, density, range, and drag coefficient.
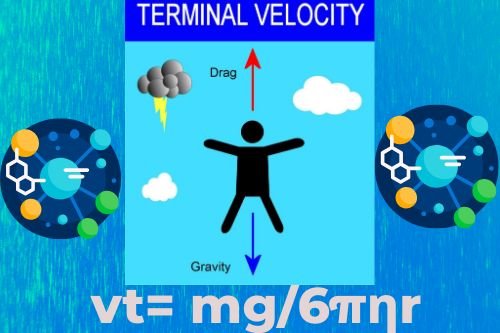
Defination?
"Terminal velocity" describes the fastest speed at which an object can descend through a liquid. This is evident when an object's downward gravitational force equals the sum of its buoyant and drag forces. Since there's no shared force pushing against the object, it's not accelerating.
Explanation:
Consider a water droplet such as that of fog falling vertically, the air drag on the water droplet increases with speed. The droplet accelerates rapidly under the overpowering force of gravity which pulls the droplet downward. However, the upward drag force on it increases as the speed of the droplet increases. The net force on the droplet is
Net force = Weight - A drag force
As the speed of the droplet continues to increase, the drag force eventually approaches the weight in magnitude. Finally, when the magnitude of the drag force becomes equal to the weight, the net force acting on the droplet is zero. Then the droplet will fall at a constant speed called terminal velocity. To find the terminal velocity v, in this case, we use Stokes. Law for the drag force.
Equating it to the weight of the drop, we have
mg = 6 πηrνt
or vt= mg/6πηr
The mass of the droplet is ρV, where volume V= ¾ (π r3)
Substituting this value in the above equation, we get V= 2gr2ρ/9η
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the terminal velocity?
An object's acceleration (or deceleration) is zero when its speed is neither increasing nor decreasing.
Q2: Terminal velocity: what is it?
The greatest velocity an object can reach when falling through a fluid is called its terminal velocity.
Q3: Who made the terminal velocity discovery?
Terminal velocity was found by Galileo.
Q4: Is there a terminal velocity in a vacuum?
In a vacuum, the terminal velocity is nonexistent since there is no drag force.
Q5: How is terminal velocity calculated?
Terminal velocity is the constant speed at which an object falls freely through a liquid or gas. When something is dropped from rest, it will accelerate until it reaches its terminal velocity; when something is compelled to travel faster than its terminal velocity, it will do so.
Q6: What is the equation for terminal speed?
Based on the thought that terminal speed is achieved when the drag force and the force of gravity are equal, terminal velocity is determined. V = square root((2 times mass times gravity)(density times range times drag coefficient)) is the equation.
Q7: The speediest speed is terminal speed, right?
The greatest speed that an object may reach is known as its terminal speed. Based on the object's normal air weight and temperature, this is often decided. Depending on the object, the final velocity varies.
What's Your Reaction?





















