What is Force its Units, Formula, Symbol and Types

Definition:
It is defined as any action that can change the position, speed, or state of an object. The act of pushing or pulling on an object is another definition. The acting force can stop a moving object, bring the object out of rest, or alter the direction of its motion.
Relation with Newton's first law:
This is based on Newton's first law of motion, which states that a thing remains stationary, or continues to move at a constant speed unless another force acts on it.
Which quantity is it?
Having magnitude and direction it is a vector quantity.
Units:
In the centigram-second (CGS unit) system of units, force is expressed in dynes.
The International Standard System of Units (SI units) is expressed in newtons (N).
| Common symbol | F |
| SI unit | Newton |
| In SI base units | kg·m/s2 |
| Other units | dyne, poundal, pound-force, kip, kilo pond |
| Derivations from other quantities | F = m a |
| Dimension | LMT-2 |
A spring balance may be a common gadget for measuring force. It employments Hooke's law, which states that the "F" on a spring is straightforwardly relative to the spring's displacement from its balance position. By joining a body to a spring and adjusting and measuring the pressure or compression of the spring, the push and pull acting on the body can be decided. A spring balance gives a numerical reading in newtons showing the sum of strength acting on the spring and in this way on the body being measured.
Equation:
The value of the "F" is expressed as the cross product of mass (m) and acceleration The condition can be communicated numerically as:
F = ma
Where, m = mass
a = acceleration
It is shown in newtons (N) or kg m/s2.
The acceleration a is given by
a = v/t
Where v = speed
t = passed time
Therefore, the above-highlighted condition can be defined as:
F = mv/t
The equation for force is p = mv.
Hence, "F" can be defined as the rate of alteration of force.
F= p/t = dp/dt
These equations are valuable for deciding the mass(m), F, increasing speed, momentum(p), and speed in a given issue.
What are the impacts of force?
In physics, movement is characterized as an alteration of position over time. In straightforward terms, movement refers to the movement of a body. As a rule, the movement can be described as:
a) a Change of speed
b) a Change of course has a few impacts, and here are many of them.
1)Force can make a steadfast body move.
2)It can stop or slow a moving substance.
3)It can increase the speed of a moving entity.
4)It can also change the direction of movement of the thing, as well as its shape and size.
Types:
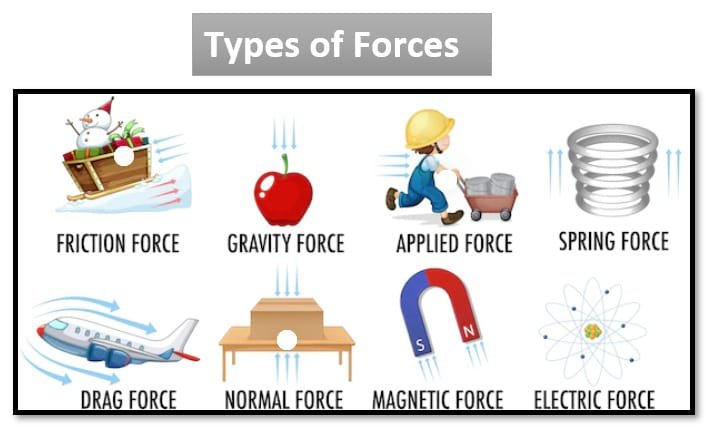 1) Contact force is the sort that happens when two objects physically touch each other or come into arranged contact. It develops due to the interaction of the surfaces of objects and acts inverse to the surfaces at the point of contact. These qualities can be appealing or horrendous, depending on the nature of the interaction.
1) Contact force is the sort that happens when two objects physically touch each other or come into arranged contact. It develops due to the interaction of the surfaces of objects and acts inverse to the surfaces at the point of contact. These qualities can be appealing or horrendous, depending on the nature of the interaction.
Here are many cases from the way of life
Door Push:
Once you push an entryway open or closed, your hand applies a contact drive to the entryway. This licenses the entryway to move against any resistance, such as contact, between your hand and the entryway.
Hit the Ball:
For case, after you hit a ball, your foot applies weight to the ball. This causes the ball to quicken and move inside the heading of influence.
I Sort in with a Compose:
After you sort in with a compose, the contact between the tip of the compose and the paper trades the ink from the compose to the paper. The weight connected to the compose makes the contact fundamental for the ink to stream onto the paper.
Walking or Running:
You're walking or running and your feet are putting weight on the ground. This gives the pounding required to push you off the ground and keep you moving.
Writing:
After you hold a book in your hand, your hand applies a compel on the book that neutralizes gravity. This maintains a strategic distance from the book from falling, making upward essentialness that equalizes the slipping drive of gravity.
Squeeze with a Wipe:
Once you press the wipe, your hand presses the wipe solidly. The contact oblige lessens the volume of the wipe and pushes the water out.
2) Non-contact force can be a sort of drive associated with an address without the requirement for physical contact between the objects included. Not at all like contact powers, which rise as a result of facilitating physical interaction, non-contact powers act at an expel. These powers can impact the advancement or behavior of an address without any physical contact.
Gravity:
This is responsible for the attraction between objects with mass. It works over long distances and is always attractive. Gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun and objects on Earth.
Electrostatic Force:
It arises from the interaction between electrical charges. Charges that resist one another and those that attract one another are similar. This can act at a distance and is responsible for phenomena such as static electricity and the behavior of charged particles.
Magnetic Force:
These are manifested through magnets or magnetic fields. They can attract or repel magnetic materials without direct contact. This force is responsible for the behavior of compass needles, the operation of electric motors, and the interaction between magnets.
Electromagnetic:
Electromagnetic combines electric and magnetic forces and is responsible for a wide variety of phenomena. This includes electromagnetic radiation (such as light) that can travel through space without physical contact.
Nuclear Force:
These are extremely strong forces acting in atomic nuclei. They are responsible for holding protons and neutrons together. These are fundamental to the stability and structure of atoms.
What's Your Reaction?





















