Lenses, their types and uses
Lenses, their types and uses
Lenses, their types and uses
What is lense?
A lens is a transparent optical device with curved surfaces that refracts or refracts light rays to converge or diverge. It is usually made of glass or clear plastic and shaped to focus or scatter light, depending on the design.
Primary types of lenses:
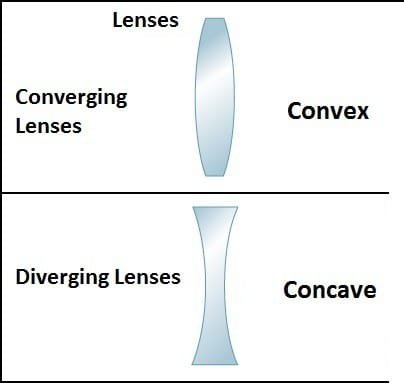
Convex lens (converging lens):
A convex lens is thickest in the center and thinnest at the edges. This causes parallel beams of light to converge or focus after passing through the lens. Convex lenses are often used in applications such as cameras, telescopes and loupes.
Concave lens (diverging lens):
A concave lens is thinnest in the center and thickest at the edges. This causes parallel rays of light to diverge or scatter after passing through the lens. Concave lenses are used to correct vision problems such as myopia (nearsightedness), and are also used in devices such as projectors and cameras to widen the field of view.
These two main types of lenses have different shapes and optical properties, allowing them to manipulate light in different ways. Convex lenses collect light rays, while concave lenses scatter them.
Different types of lenses:
Lenses can be divided into different types based on different criteria. Here are some common types of lenses based on their features and uses:
Spherical Lens:
Spherical lenses have curved surfaces that can be convex or concave. They are the most common type of lenses and are used in everyday optical devices such as cameras and eyeglasses. Spherical lenses can be biconvex (both surfaces are convex), biconcave (both surfaces are concave), or plano-convex/concave (one surface is flat).
Aspherical Lenses:
Aspherical lens surfaces deviate from a perfect sphere. Unlike spherical lenses, aspherical lenses have a different surface curvature. They are designed to reduce spherical aberrations and improve image quality. Aspherical lenses are used in cameras, telescopes and corrective glasses.
Cylindrical Lens:
Cylindrical lenses have curved surfaces in one direction and a flat surface in the perpendicular direction. They are often used to correct astigmatism, a vision condition that causes blurry or distorted images due to an irregular shape of the cornea or lens. Cylindrical lenses are also used in optical systems to change the shape of a light beam.
Fresnel Lens:
Fresnel lenses are thin flat lenses with concentric grooves on one or both sides. These grooves reduce the thickness and weight of the lens while maintaining focus capabilities. Fresnel lenses are often used in applications where conventional thick lenses would be impractical, such as lighthouses, overhead projectors and solar concentrators.
Meniscus Lens:
Meniscus lenses have a convex surface and a concave surface. The curvature of the two surfaces can differ, resulting in positive (convex-concave) or negative (concavo-convex) meniscus lenses. These lenses are used to correct aberrations and improve image quality.
Zoom Lens:
A zoom lens is a type of lens that allows the focal length to be changed, allowing the user to adjust the magnification and field of view. It offers the flexibility to go from wide angle to telephoto without switching lenses. Zoom lenses are commonly used in cameras and camcorders.
Telephoto lenses:
Telephoto lenses having a narrower field of view and the ability to close in on distant objects because their focal length is longer than their actual length. They are widely used in sports and wildlife photography to capture distant subjects.
Macro lens:
Macro lenses are specially designed for close-up photography and provide high magnification and sharp focus on small subjects. They enable photographers to capture intricate detail and achieve zoom ratios of 1:1 or greater.
These are just a few examples of lens types based on their features and uses. Lenses can vary greatly in design and purpose, meeting different optical needs in different industries and applications.
Uses of lens:
Lenses have many uses in different fields and industries. Here are some common uses for lenses:
Photography and video filming:
Lenses are important parts of cameras and camcorders. They enable photographers and videographers to direct light onto the camera's sensor or film to capture still images and video. Different lenses offer different focal lengths, aperture sizes and optical properties, providing a wide range of creative options for landscapes, portraits, macro photography and more.
Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses:
Lenses are used in eyeglasses to correct vision problems. Convex lenses are used to help people with farsightedness (hyperopia), while concave lenses help people with nearsightedness (myopia). These lenses change the path of light entering the eye, allowing it to focus properly on the retina and providing clearer vision. Contact lenses work in a similar way, but they are placed directly on the surface of the eye.
Microscopes:
Microscopes use lenses to magnify and observe small objects or samples. Compound microscopes usually have several lenses, including an objective lens and an eyepiece lens, that work together to magnify the specimen and produce a detailed image. Lenses are critical to achieving high magnification and resolution of microscopic detail.
Telescopes:
Telescopes use lenses (or mirrors) to collect and focus light from distant celestial bodies. Telescope lenses help magnify and improve the visibility of stars, planets, galaxies and other astronomical phenomena. They enable astronomers and astronomers to study and observe objects in the night sky.
Projectors:
Lenses play a vital role in projectors by focusing and directing light onto a screen or surface, creating magnified images or videos. Projector lenses help ensure that the projected image is sharp, clear and properly scaled to the correct size.
Eyepieces:
Eyepieces are lenses used in various optical instruments such as binoculars, spotting scopes, and microscopes. They are located next to the eye and help to magnify and focus the image created by the primary lens or lens.
Laser systems:
Lenses are used in laser systems to control the direction, focus, and spread of laser beams. They help shape and manipulate laser light for a variety of applications, including laser cutting, engraving, medical procedures, scientific research and telecommunications.
Magnifying Glasses:
Convex lenses, often in the form of portable magnifying glasses, are used to magnify small objects and text, making them easier to see. They are often used for reading fine print, scrutinizing details, and performing tasks that require high visibility.
These are just a few examples of the many practical uses of lenses. Lenses are essential in a wide variety of optical devices, scientific instruments, medical equipment and everyday objects that rely on the manipulation of light to achieve specific goals.
What's Your Reaction?





















