Non-Conventional Energy Sources
Non-conventional energy sources like tides, waves, and solar energy are expected to significantly contribute to future energy demand, offering long-lasting, low-cost solutions for powering satellites.

Non-Conventional Energy Sources
Conventional Sources of Energy are also known as non-renewable energy sources and are available in limited quantities apart from hydroelectric power.
These are the energy sources which are not very common these days. However, it is expected that these sources will contribute substantially to the energy demand of the future. Some of these are introduced briefly here.
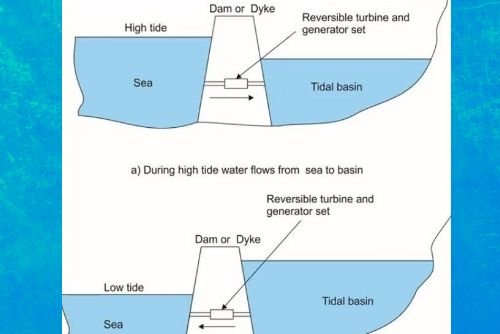
Energy from Tides:
One very novel example of obtaining energy from the gravitational field is the energy obtained from tides. The gravitational force of the moon gives rise to tides in the sea. The tides raise the water in the sea roughly twice a day. If the water at the high tide is trapped in a basin by constructing a dam, then it is possible to use this as a source of energy. The dam is filled at high tide and water is released in a controlled way at low tide to drive the turbines. At the next high tide, the dam is filled again and the rushing water also drives turbines and generates electricity.
Energy from Waves:
The tidal movement and the winds blowing across the surface of the ocean produce strong water waves. Their energy can be utilized to generate electricity. A method of harnessing wave energy is to use large floats that move up and down with the waves. One such device invented by Professor Salter is known as Salter's duck (Fig. 4.14). It consists of two parts (i) Duck float. (ii) Balance float. Duck float moves relative to the balance float by the wave energy. The relative motion of the duck float is then used to run electricity generators.
Solar Energy
The Earth receives a huge amount of energy directly from the Sun each day. Solar energy at normal incidence outside the Earth's atmosphere is about 1.4 kWm2 which is referred to as the solar constant. While passing through the atmosphere, the total energy is reduced due to reflection, - scattering, and absorption by dust particles, water vapors, and other gases. On a clear day at noon, the intensity of solar energy reaching the Earth's surface is about 1kWm². This energy can be used directly to heat water with the help of large solar reflectors and thermal absorbers. It can also be converted to electricity. Collectors are used for heating water, in one method the flat plate. c. It has a blackened surface which absorbs energy directly from solar radiation. Cold water passes over the surface and is heated up to about 70°C.
Much higher temperature can be achieved by concentrating solar radiation on a small surface area by using huge reflectors (mirrors) or lenses to produce steam for running a turbine. The other method is the direct conversion of sunlight into electricity through the use of semiconductor devices called solar cells also known as photo voltaic cells. Solar cells made from silicon are thin wafers. To create a voltage, electrons in the silicon gain energy from sunlight. The voltage produced by a single voltaic cell is very low. In order to get sufficient high voltage for practical use, a large number of such cells are connected in series forming a solar cell panel.
For cloudy days or nights, electric energy can be stored during the Sunlight in Nickel-cadmium batteries by connecting them to solar panels. At night or on cloudy days, these batteries can then provide power to electrical appliances Solar cells, although, are expensive last a long time, and have low running costs. Solar cells are used to power satellites having large solar panels that are kept facing the Sun. Other examples of the use of solar cells are remote ground-based weather stations and rainforest communication systems. Nowadays solar calculators and watches are also in use.
Energy From Biomass
Biomass is a potential source of renewable energy. This includes all the organic materials such as crop residue, natural vegetation, trees, animal dung, and sewage. Biomass energy or bioconversion refers to the use of this material as fuel or its conversion into fuels. There are many methods used for the conversion of biomass into fuels. But the most common are
1. Direct combustion
2. Fermentation
The direct combustion method is usually applied to get energy from waste products commonly known as solid waste. It will be discussed in the next section.
Biofuel such as ethanol (alcohol) is a replacement for gasoline. It is obtained by fermentation of biomass using enzymes and by decomposition through bacterial action in the absence of air (oxygen).
The rotting of biomass in a closed tank called a digester produces Biogas which can be piped out to use for cooking and heating.
The waste material of the process is a good organic fertilizer. Thus, the production of biogas provides us energy source and also solves the problem of organic waste disposal.
Energy from Waste Products:
Waste products like wood waste, crop residue, and particularly municipal solid waste can be used to get energy by direct combustion. It is probably the most commonly used conversion process in which waste material is burnt in a confined container. The heat produced in this way is directly utilized in the boiler to produce steam that can run a turbine generator.
Geothermal Energy
This is the heat energy extracted from inside the Earth in the form of hot water or steam. Heat within the Earth is generated by the following processes.
1. Radioactive Decay
The energy, heating the rocks, is constantly being released by the decay of radioactive elements.
2. Residual Heat of the Earth
In some places, hot igneous rocks, usually within 10 km of the Earth's surface, are in a molten and partly molten state. They conduct heat energy from the Earth's interior which is still very hot. The temperature of these rocks is about 200°C or more.
3. Compression of Material
The compression of material deep inside the Earth also causes the generation of heat energy.
In some places, water beneath the ground is in contact with hot rocks and is raised to high temperatures and pressure. It comes to the surface as hot springs, geysers, or steam vents. The steam can be directed to turn turbines of electric generators.
At places, where water is not present and hot rocks are not very deep, the water is pumped down through them to get steam. The steam then can be used to drive turbines or for direct heating.
Geyser is an interesting phenomenon of geothermal energy. It is a hot spring that discharges steam and hot water, intermittently releasing an explosive column into the air. Most geysers erupt at irregular intervals. They usually occur in volcanic regions. Extraction of geothermal heat energy often occurs closer to geyser sights. This extraction seriously disturbs the geyser system by reducing heat flow and aquifer pressure. The aquifer is a layer of rock holding water. This allows water to percolate through it with pressure.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What's Your Reaction?





















